This post may contain affiliate links. Please read our disclosure.
The onset of diabetes can be dangerously quick, and extremely risky to your health and life.
If you’re experiencing diabetes symptoms, such as extreme hunger and thirst, weight loss, frequent urination, blurry vision, and fruity-smelling breath, you should be tested for diabetes as quickly as possible.
Getting tested for diabetes is the only way to tell for sure if you have the condition.

Who should get tested for diabetes?
If you’re thinking about getting tested for diabetes, then you probably should, as there are very few risks to getting tested.
There are few false “positives”, it’s inexpensive, easy, and can bring you peace of mind.
A few reasons to get tested for diabetes are:
- You have a family history of the disease (type 1 or type 2)
- You have several risk factors for the disease, including but not limited to: living a sedentary lifestyle, being overweight or obese, being over the age of 45, or you live with high blood pressure or heart disease
- You are experiencing diabetes symptoms, including but not limited to: rapid weight loss, extreme thirst, frequent need to urinate, blurry vision, extreme fatigue, or fruity-smelling breath
- You currently have prediabetes
- You are pregnant and have a family (or personal) history of gestational diabetes
Because it’s possible to have prediabetes or type 2 diabetes with few or no symptoms, it’s recommended to have a blood test done at your annual doctor’s visit or to test your blood sugar yourself with a home test every year if you are in a high-risk group.
How hard is it to get tested for diabetes?
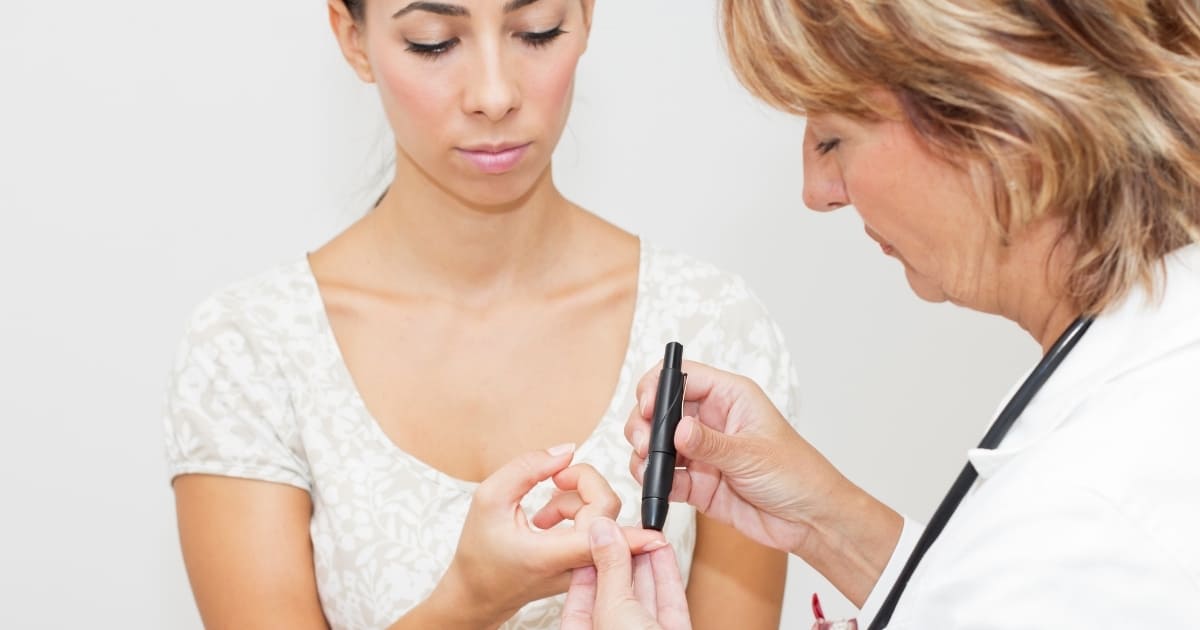
Getting tested for diabetes is extremely easy, and it can be done with a blood test either at home or in your doctor’s office.
There are two different types of blood tests that can be used to detect diabetes:
Finger stick test
A finger stick test is done with a glucometer that can be bought over the counter at any local pharmacy and done at home or in a doctor’s office.
The test measures what your blood sugar is right now. Normal blood sugar levels for people who don’t have diabetes are:
- Fasting blood sugar (in the morning, before eating): Less than 100 mg/dL
- 1-2 hours after a meal: Less than 140 mg/dL
- 2-3 hours after eating: Less than 100 mg/dL
If your glucose level is higher than 100 mg/dL more than 2 hours after eating, you most likely have diabetes or prediabetes.
However, a certain diabetes diagnosis can only be made after a more accurate lab test, so you should always see your doctor immediately if your blood sugar is high.
You can buy a glucometer with 100 fingersticks on Amazon for $25 to test your blood glucose regularly yourself.
HbA1c test
An HbA1c test is the main blood test used to diagnose diabetes. It measures your average blood sugar level over the previous 3 months.
You can have the test done at the doctor’s office or use a test kit to measure your A1c at home.
The American Diabetes Association has established the following A1c guidelines for using the test as part of a diabetes diagnosis:
You can buy an A1c Test Kit on Amazon for $65.
The home test kit is very easy to use as demonstrated in this short video:
If your A1c test indicates that you have diabetes or pre-diabetes, immediately see your doctor for further tests and to start a treatment program.
Testing for gestational diabetes
There is a routine oral glucose tolerance test given to all pregnant women at around 28 weeks gestation, where you drink a sweet glucose liquid (that usually contains around 50 grams of sugar!), and the doctor will measure your post-prandial blood glucose level (with a finger stick test) a few hours later to see how your body (and pancreas) responds.
Gestational diabetes rarely develops before 26-28 weeks gestation, but if you’re worried about insulin resistance and the onset of diabetes earlier than that, the test can be ordered early.
If you are pregnant and getting tested for gestational diabetes via the oral glucose tolerance test, a blood sugar under 140 mg/dL two hours after drinking the liquid is normal, a blood sugar between 140-199 mg/dL indicates prediabetes, and a reading of 200 mg/dL or higher indicates gestational diabetes.
Doctors will typically do these tests twice if they feel there’s been a mistake or to confirm a diagnosis.
Are the tests accurate?
It is possible to have diabetes but test negative on these blood tests (it may just mean that you’re currently experiencing a low blood sugar!), or that you do not have diabetes but your blood sugar tested higher than normal (perhaps you forgot to fast for a fasting blood sugar test).
There are always outliers, and that is why sometimes doctors like to repeat tests before making a definitive diagnosis.
However, unless a glucometer is malfunctioning or there is miscommunication in the laboratory, these tests are very reliable and can almost always indicate a diabetes diagnosis with precision.
Can these tests tell you what type of diabetes you have?
No, only that you have diabetes. Treatment can depend on the type of diabetes you have, so knowing which type you have is important.
Many doctors will only look at the patient’s age, weight, and family history to diagnose the type of diabetes.
This leads to a lot of people who are older than 30 at the time of diagnosis or overweight being misdiagnosed as type 2 when they in reality have type 1 diabetes or LADA (Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults).
If you are diagnosed with type 2 diabetes, it’s highly recommended to also have an “autoantibodies” test made. Autoantibodies are proteins that are present when your immune system begins attacking itself, resulting in an autoimmune disease.
If autoantibodies are present, you have type 1 diabetes or LADA and will need a different treatment regime than if you had type 2 diabetes.
How expensive are these tests?
The good news is that getting tested for diabetes can be really quite simple and not too expensive. If you want to test in the comfort of your own home, you can buy a glucometer over-the-counter at any pharmacy or on Amazon for $25-$30.
An A1c home testing kit with 4 tests is around $65 on Amazon.
You may also get a rapid glucometer test at your primary care physician’s office, but will need to pay a copayment for being seen, and that cost depends on your health insurance coverage.
Getting an HbA1c test at the doctor’s office is pretty routine, but the cost will depend on what type of insurance you have. Lab services are usually run for a copayment of between $5-50.
Without insurance, this is all much more expensive, but if you feel like you might have undiagnosed diabetes and do not have insurance, go to your local emergency department for immediate medical attention.
Should you test kids who are predisposed to diabetes?
Yes! You may be worried about your child or children developing diabetes if you live with the condition yourself.
This is reasonable: according to the American Diabetes Association, if you are a man living with type 1 diabetes, the odds of your child getting type 1 diabetes are 1 in 17. If you are a woman who has type 1 diabetes, and you gave birth to them before you turned 25, the risk is 1 in 25.
If you birthed your children after age 25, your children’s risk is 1 in 100, which is about the same as the general population.
Luckily, now there are antibody tests available to determine risk for children, specifically if they have a sibling in the family who has type 1 diabetes. These tests measure antibody response to insulin, the islet cells of the pancreas, or to an enzyme called glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD).
A high level of antibody response indicates that a child has a higher likelihood of developing type 1 diabetes, but it doesn’t guarantee that they will.
If you live with type 2 diabetes or have type 2 diabetes in your family, the likelihood of your children developing type 2 diabetes is also increased, but not guaranteed.
Talk with your doctor if you’re interested in requesting an antibody test for your children, especially if you or their sibling already live with diabetes.
Frequently asked questions
If you’re experiencing diabetes symptoms, such as extreme hunger and thirst, weight loss, frequent urination, blurry vision, and fruity-smelling breath, you should be tested for diabetes as quickly as possible.
Yes, diabetes can be detected easily during a routine blood test.
Yes, you can test for diabetes at home with a fingerstick test or an HbA1c test that can be bought online. However, you should always contact your medical team immediately if you test positive so they can do additional tests to confirm your diagnosis and start you on a treatment program.
Yes, but they are not as accurate as blood tests and aren’t used for diabetes screening anymore
Summary
As the rates of type 1, type 2, and even gestational diabetes continue to rise in the United States, it’s more important than ever to make sure you know how to get tested for diabetes, if you feel like you may have an undiagnosed case of the condition.
The only definitive way to diagnose diabetes is through a blood test, measuring the amount of glucose in the blood in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), and that can be done either by measuring your Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) in a laboratory, or with a rapid fingerstick test, measured on a glucometer.
People who are pregnant are routinely tested for gestational diabetes between 26-28 weeks gestation with an oral glucose tolerance test.
Depending on your health insurance, getting tested for diabetes is easy and relatively inexpensive.
However, if you’re experiencing diabetes-like symptoms for several days and feel sick, seek emergency medical attention immediately.
Especially if you’re experiencing rapid weight loss, extreme thirst, fatigue, blurry vision, fruity-smelling breath, and frequent urination, as these are classic diabetes symptoms that need to be addressed immediately by health professionals.