Diabetes is one of the most common diseases in America. Roughly 1 in 10 of us are living with this life-altering condition, and around 95% percent of that 1 in 10 are considered Type 2.

Although many of us have heard of the term “diabetes”, most of us still don’t know what the symptoms are or how to manage the condition. In fact, diabetes is ranked 8th in the Leading Causes of Death statistics in America.
Understanding what your diagnosis means and how to manage the disease can help you stay healthy and live a long happy life.
Type 2 diabetes

We will start this guide by explaining what Type 2 diabetes is, the symptoms to look out for, and the treatments you can receive. Having a strong foundation of knowledge can keep you alert to the dangers you may face.
What is type 2 diabetes?
Both Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes are connected to your pancreas’s inability to make insulin.
The pancreas is an organ located near your liver. It is technically part of the small intestine, and it has two jobs. The first is to produce enzymes that help move food through your digestive system.
The second job is to create hormones. Most importantly, it produces hormones that regulate your blood sugar, such as insulin and glucagon. People with diabetes have a pancreas that is failing at this second job.
In Type 1 diabetes, the pancreas cannot create insulin. With no insulin in the bloodstream, the person’s body cannot break down the glucose (or sugar) in their body. Their blood sugar levels become too high, which causes dehydration, blurry vision, and stops cuts from healing.
In Type 2 diabetes the same effects can happen. The difference is in the cause. This version of the disease is created by several lifestyle choices working against you (and genetic predisposition for the disease). We will go into more detail about that later, but these lifestyle choices cause the body to become resistant to insulin.
When the body is consuming or holding on to too much sugar, it cannot perform its job as needed.
With so much to work with, the pancreas creates more insulin to keep your blood sugar levels healthy. The insulin’s job is to tell cells to accept the sugar as fuel. Over time the cells stop listening to this command due to over-exposure, making them “insulin resistant”. As time goes on, more and more cells stop listening to the command, making it harder and harder for the pancreas to keep your blood sugar at a healthy level.
It’s at this point that you start noticing the symptoms of Type 2 diabetes.
Symptoms
As we said before, the symptoms of Type 2 diabetes are very similar to Type 1. However, Type 2 patients tend to experience these symptoms getting slowly worse over time.
As Type 2 is created through years of excess sugar in the system, it may take just as long to notice the gradual change.
The symptoms of Type 2 diabetes are:
- Fatigue or sleepiness.
- Blurred vision.
- Constantly thirsty or hungry.
- A slowed healing response to sores and cuts.
- Needing to urinate or go to the toilet more often (especially at night).
- Losing weight unexpectedly
- A numbness or tingling sensation in your feet or hands.
If you notice any of these symptoms talk to your medical professional. They will likely note your diabetes-based concerns and perform tests to confirm or deny the theory.
How is type 2 diabetes diagnosed?
There are 3 tests that doctors use to diagnose diabetes. The different methods allow the medical professionals to create fast but non-specific results or slow but specific results. They also allow a variation in testing methods for those with allergies or aversions to medications.
A1C tests
A1C, also known as hemoglobin A1C, tests the amount of glucose connected to your hemoglobin.
Hemoglobin is the protein inside red blood cells which carries oxygen around the body. We need glucose in the hemoglobin to give us energy, but when there’s too much our body becomes poisoned by the excess.
During the test, a health care professional will use a small needle to take a blood sample from your arm (or just a drop of blood from your fingertip).
If you come back with a percentage of 5.7% or less, it means your blood sugar levels are healthy.
Results of 5.7% to 6.4% are in the amber zone. You are at risk of diabetes or have developed prediabetes. At this point, you can follow preventive measures to bring your blood sugar level down.
However, a percentage of 6.5% or higher means you have diabetes. The higher this number becomes, the more dangerous it is to your health.
FPG tests
FPG, also known as Fasting Plasma Glucose, is more accurate than A1C. Instead of working with averages of your typical months, FPG learns what your baseline glucose levels are without the variable of food.
For this test to work, the patient needs to fast for at least 8 hours. This means no eating and no drinking. Either a needle will be used or your skin will be pricked to produce a single drop of blood (similar to the A1C test).
From this test, the doctors can see exactly how much sugar is in your blood. Measured in milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL), a normal blood sugar level will be between 70 mg/dL and 99 mg/dL.
Prediabetes ranges between 100 mg/dL and 126 mg/dL. Anything over 126 mg/dL means the patient has diabetes.
OGTT tests
OGTT, also known as the Glucose Tolerance Test, is often the best choice for children. This is because it has the same accuracy as the FPG, but without fasting.
Instead, a sample of blood is taken to see what the patient’s glucose level is without interaction. The patient is then given a sugar drink. This drink will contain 75 grams of glucose.
After 30 minutes, another blood sample is collected. This continues for 3 hours, as the medical professional evaluates how the patient’s blood is handling the sugar.
By the end of the examination, if the patient has less than 140 mg/dL of glucose, they have responded normally. Between 140 mg/dL and 199 mg/dL is a sign of prediabetes. 200 mg/dL or more will diagnose diabetes.
Causes
There is more than one way to develop Type 2 diabetes. A combination of the risk factors below will make you more at risk for this disease. Some of the risk factors are genetic, while others are through lifestyle choices.
This means people who have a fit and healthy lifestyle can still develop Type 2 diabetes, if their biology predisposes them to the disease.
Genetic Risk Factors
- Family History
If someone in your family has Type 2 diabetes, you are more likely to develop the disease. Your genetics may be predisposed to the disorder.
- Ethnicity and Race
The reason is still unclear, but White people are less likely to develop Type 2 diabetes than Asian, Hispanic, and Black ethnicities.
- Age
As you get older, parts of your body are expected to strain or become tired. By the time you reach 45, your likelihood of developing diabetes increases.
- Polycystic Ovary Syndrome
POS is a hormonal condition that causes the female body to produce excessive androgen. Although its main features are irregular periods, extreme cramps, and excessive hair growth, the increased androgen can confuse the body’s receptor signals causing insulin resistance.
- Abdomen Fat Storage
If your figure holds its weight around your stomach, then your body may not be distributing fat evenly. Ideally, the excess fat on your body should be evenly stored around your hips and thighs too. An intense fat collection around your middle means intense insulin resistance too.
Lifestyle Risk Factors
- Overweight
Being overweight means you may be consuming more sugar than your body can manage.
- Inactivity
Physical activity pumps the blood around your body and forces your muscles into needing more energy. This makes them insulin sensitive, meaning they need more insulin. When you don’t exercise, the lack of energy needed to keep the blood moving has the opposite effect.
Treatment
There are many different ways to treat Type 2 diabetes. The first is a healthy diet and regular exercise. As we said before, exercise forces the body into needing insulin, thereby using up the glucose in your blood. And, when you’re eating healthily, you will be digesting less sugar, slowing down the glucose intake.
The next treatment is through oral medication. Metformin, Sulfonylurea, and Thiazolidinediones are the most popular forms of Type 2 diabetes medication. Depending on your specific needs, your doctor will prescribe a drug that either lowers your glucose production (Metformin), increases your insulin production (Sulfonylurea), or stimulates insulin sensitivity in your cells (Thiazolidinedione).
If oral medication isn’t effective in controlling blood sugar levels, injected insulin may be the next step in the treatment plan.
Read more: Is Type 2 Diabetes Reversible
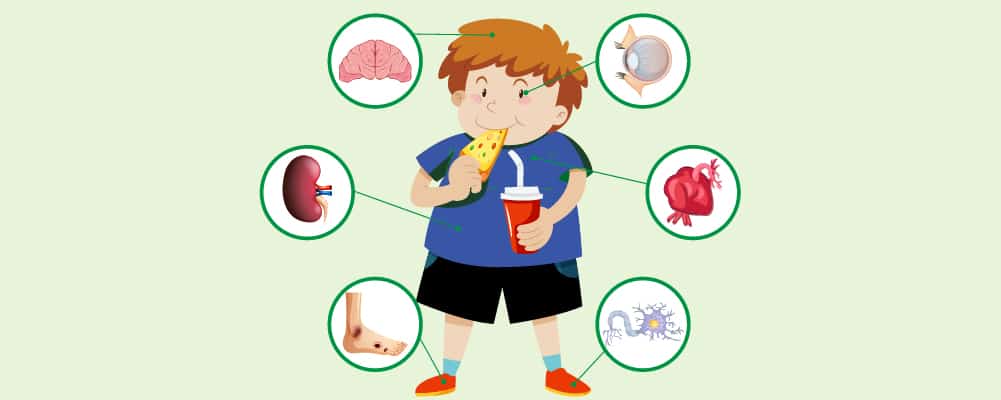
How type 2 diabetes can affect you in the long term
We have discussed the symptoms of Type 2 diabetes, but the long-term effects of the disease can cause more damage over time. When left untreated, you can experience the following long-term effects.
Risk of cardiovascular diseases
“Cardiovascular” is a term that relates to your heart and your blood vessels. Cardiovascular disease is when your body creates a condition in this area of the body, such as a stroke or a heart attack.
People with diabetes often have high blood pressure due to their crowded blood vessels, filled with excess glucose. With high blood pressure comes a risk of cardiovascular disease, as your blood cannot travel around your body smoothly. This can create blood clots, which result in a stroke.
Diabetes-related eye problems
There are four main eye problems that are related to diabetes – cataracts, glaucoma, macular edema, and retinopathy.
Most people don’t develop these conditions in the early stages of diabetes. However if left untreated, you can experience dots in your vision, or flashes of lights. When this happens you need to call a doctor immediately.
Cataracts are when the lens over your eyes becomes cloudy. This can happen due to old age, but those with diabetes can develop this condition much earlier in their life.
Glaucoma is when there is too much fluid in the eye. The pressure damages your eye and can eventually cause blindness.
Macular edema is when your retina swells. It causes your vision to become blurry. Getting treatment as soon as possible can help you avoid sight loss.
Retinopathy is when the blood vessels in your eyes become damaged. It can cause blurry eyesight or even a lack of vision completely. Unlike the other conditions, retinopathy can go unnoticed for years before becoming a concern. This is why those with diabetes need to get their eyes checked as often as possible.
Catching these conditions early will give you a greater chance to keep your eyesight.
Kidney disease
The kidney’s job is to clean your blood and remove any toxins. Any toxins found are turned into urine. Kidney disease is when the blood vessels connecting to the organ are damaged. Like a double-edged sword, the beginning stages of this disease are painless. You will only see the symptoms (such as blood in your pee) when it’s advanced.
Those with diabetes are more likely to damage their blood vessels due to the excessive amount of glucose in their blood. For this reason, patients need to have kidney disease screenings regularly, to find and treat the condition before it turns into a painful health issue.
Neuropathy
Neuropathy is a dysfunction of your nerves. It often presents itself as numbness or weakness in your limbs. Caused by high blood glucose levels, you may notice a lack of feeling in your stomach, chest, hands, feet, legs, and arms.
If left untreated, the nerves that control your organs can be affected too. Talk to your doctor if you notice numbness in your body.
Dry skin
Compared to neuropathy diseases and possible sight loss, dry skin may not seem like a big issue. However, extremely dry skin will result in a broken protection barrier. Your skin is needed to keep infections away, but if it’s dry, it will become harder to heal any cuts you have. This means you will be more susceptible to bacteria and viruses.
Tooth decay and gum infections
Just as dry skin can result in infection, the lack of healthy blood vessels in your mouth can cause gum infections too. Your teeth are connected to blood vessels, but through diabetes, this connection can be disconnected leading to rotting teeth and damaged gums.
Increase in stress, depression, and anxiety
Understanding the risks your body is facing can be a massive source of anxiety and stress. As your stress levels increase, as does your heart rate. With an elevated heart rate, your blood will be pushed around your body faster, creating high blood pressure.
The high blood pressure then speeds up the deterioration of your blood vessels causing the medical issues above.
Like a spiral of negativity, the stress of ill health creates ill health, causing more stress.
10 tips for managing type 2 diabetes

Although medication is the best way to manage your Type 2 diabetes, it cannot help your blood sugar levels by itself. Your body needs you to actively change your lifestyle habits to create an environment of insulin repair.
We have 10 tips to help you manage your diabetes. When you’re feeling lost and overwhelmed, come back to this page and remind yourself how you can find stability again.
Create a balanced diet
People with Type 2 diabetes should avoid processed foods such as chicken nuggets and burgers. These food types create high cholesterol, which can add more pressure to your blood vessels.
Instead, you should be eating 5 portions of low-carb fruit and vegetables a day (a portion is roughly a handful) – making it the biggest food group of your day.
Ideally, you should have a portion of protein, such as meat, fish, or beans, every day too. Oily fish is the preferred protein due to its omega value.
The problem most of us have is portion sizes. Many of us know what a healthy meal looks like, but our plates and bowls are becoming bigger and bigger as the decades go on. To help you create a healthy portion size, buy a small bowl. When you plate up your food, the portion will look heaped – giving the illusion of a large meal.
Another tip is to eat slowly. Eating slowly will allow your stomach to digest the food, and learn when it’s full. Giving it time to reach this conclusion can help you reduce your portion size.
Exercise frequently
Everyone should be exercising frequently. But, because those with diabetes have a high risk of cardiovascular disease, they need to ensure a healthy blood pressure to keep their risk low.
To keep the oxygen flowing, you should be participating in aerobic exercise. This is any type of exercise that increases your heart rate. Depending on your current fitness level, you may want to start walking for 30 minutes every day. Once walking no longer creates an increase in your heart rate, try swimming or jogging.
Generally speaking, you need to exercise for 150 minutes a week (or 30 minutes every weekday), and that exercise should raise your heart rate. As you get stronger, you can create more vigorous routines to keep improving your fitness level.
Manage weight loss
With a healthier diet and an increase in exercise, you should begin to lose weight. However one of the symptoms of Type 2 diabetes is unexplained weight loss. If you start noticing a reduction in size that doesn’t match the amount of exercise you are putting in, you should see a doctor.
They will confirm if you happen to have hit a stride in your weight loss routine, or if something else is at play.
Of course, mismanaged weight isn’t the only cause of Type 2 diabetes. As we discussed before, genetic factors such as POS could have caused your diagnosis. If your diabetes isn’t connected to your weight, then don’t push to lose more.
Get frequent check-ups

A lot of the serious issues that can develop due to diabetes, take a while to present themselves. If left unchecked, your kidneys could be silently suffering without your knowledge. To make sure that these hidden illnesses don’t spread, you should visit a medical professional regularly.
Kidney disease screening, dentists’ check-ups, optician check-ups, and heart disease screenings should become a normal 6-month operation.
Unfortunately, these checkups can cost a lot of money, which is why some people with diabetes don’t schedule a regular screening. However, avoiding these lifesaving checks will cost more in the long run, as surgery and extra medication will be needed to keep you healthy.
Manage stress effectively
One of the biggest issues a newly diagnosed diabetic faces is an increase in stress. With new medications and the daunting prospect of pain in your future, if you don’t manage your condition well, it can be easy to fall into a pit of despair.
First, we suggest letting go of the past. It doesn’t matter what got you to this point, now is the time to focus on change. Let go of any judgments you have about your diet or exercise routine, and instead focus on how you can improve them.
Accept that you cannot change the path that leads you to diabetes, and recognize that you do have the power to change this part of your story.

If you feel a wave of anxiety coming, try these three stress management tips.
Number one – deep breathing. Start by either lying on the floor, allowing your whole body to relax or allowing your feet to lay flat on the ground as you sit on a chair. Then take a few deep breaths. In through your nose, hold, and out through your mouth. Do this for a couple of minutes to help your breathing return to normal.
Number two – relaxation stretches. Either lie down or sit comfortably on a chair. Focus on your toes and clench them. Hold the clench for 5 seconds, and then relax. Do this again to your calves, hold for 5 seconds and then relax. Keep doing this as you slowly travel up your body. Eventually, your physical self will be soaking in a relaxing tingle.
Number three – exercise. If you have the time to truly step away from everything and go for a walk, or drive to the gym, then take this moment to go. Exercise releases endorphins. Even though most of us don’t feel like exercising when we are feeling low, you will notice an improvement in your mental health once you get your blood pumping.
Lower your alcohol intake
When you drink alcohol, you are digesting a substance that contains a high amount of sugar. People without diabetes normally monitor their alcohol intake to avoid weight gain from this sugar. But those with diabetes, need to consider how alcohol can affect their glucose levels.
With a mass increase in sugar, your body will likely go into a hypoglycemic state – or a hypo. This causes your body to shake, your vision to blur, and an inability to think clearly.
Avoiding alcohol can help you stay clear of these disorienting attacks.
Stop smoking
Smoking not only harms your blood flow due to the digestion of tar, but it can also cause Type 2 diabetes. Around 30 to 40% of people who smoke cigarettes develop Type 2 diabetes.
Due to the additional harm smoking does to the body, these patients are more likely to develop the serious health problems we want to avoid. Strokes, heart disease, neuropathy, and retinopathy all become more likely when a diabetic smokes.
Stopping smoking is harder than many people give credit for. If you need help with this journey, call the free government advice line at 1-800-784-8669, or visit their website CDC.gov/tips.
Find a support group
During this experience, you’re going to feel overwhelmed. It’s okay. You’re not alone.
You may find it helpful to talk to other people going through the same thing as you. There are millions of people around the world managing their Type 2 diabetes, and many of these people join community support groups to lift each other up when they are feeling down.
Joining these communities can help you stay focused on your healthy eating or exercising routine. They can help you discover new recipes for a healthy and tasty snack that can power you through the day without having a hypo attack.
They can also share their own life experiences – helping you understand what your recovery could look like or how to avoid pressures such as drinking alcohol or smoking.
Generally speaking, there are two types of support groups – online and in-person.
Online forums such as DiabetesSisters have the benefit of constant availability. The larger the platform, the more likely someone will be there in your moment of need. Send an instant message to reach for support.
You will also find online education services to teach you more about your illness and how to manage it.
In-person support groups, such as Defeat Diabetes Foundation, allow you to meet up with people in your area and have real connections with those going through the same issues. In our digital age, many of us recognize that face-to-face contact can help us feel calmer, connected, and understood.
If you are looking for recommendations on support groups, talk to your doctor about local and respected options.
Think positively
When you are first given your Type 2 diabetes diagnosis, it can be easy to fall into a downward spiral. But if you concentrate on the positive, you can push through this illness and aim towards stability.
Reading a webpage telling you to think positively might sound cheap, but we have science to back up positive thinking.
First, you need to understand what positive thinking actually means. When unpleasant situations come your way, your instinct might be to worry or fret. However, with positive thinking, you force yourself to see the light at the end of the tunnel.
For example, with a diabetes diagnosis, you may reflect on how poor lifestyle choices may have contributed to the disease. But with positive thinking, you may see this as a sign to finally take up that swimming class you always talk about.
Always searching for the light will help you become productive, but there are more benefits than that. Embracing optimism helps you achieve lower blood pressure. This is because, over time, you manage to reduce your stress response, lowering your “fight or flight” hormones, and relaxing your muscles.
With lower blood pressure, you can say that positive thinking literally reduces your chances of heart attacks and strokes.
Take small steps

Lastly, we need to remind you that making a lifestyle change doesn’t happen overnight. You can’t successfully sign up for gym classes, change your diet and keep an active screening schedule all on the same day.
Even if you manage to set up these goals, you will be asking your mind to jump over a lot of hurdles all in quick succession.
Instead, you should figure out what the easy goals are first, and go from there. If walking during your lunch break adds a new level of exercise to your routine, then make it your first goal. Once that feels normal, look at your life again and see where other changes could be made.
Summary

Managing your Type 2 diabetes diagnosis can only begin when you understand how the disease developed and the risks that come when it’s left unchecked.
If you are an active person but have a sweet tooth, you know that managing your diabetes doesn’t mean working out more. Instead, you need to change your diet. Keeping on top of these healthy changes can help you prevent further escalation into diabetes – reducing your risk of heart disease, neuropathy, and blindness.




Kate petrie
How do I know if my glucose is high will I need to test it.
Christel Oerum, MS
Yes, the only way to truly know if your blood sugar is elevated is to do a test. You can do that at home with a glucometer